
In the report, which is updated every three months by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and includes data on the global economy, it is observed that the global recovery has slowed down due to the increasing disparities between economic sectors and regions. Therefore, the global growth projected at 3.5 percent in 2022 forecasts is expected to decline to 3.0 percent in the rest of 2023 and in 2024.
Although the rates in the July report are slightly higher than expected compared to April, they paint a weak picture by historical standards. On the one hand, the Central Bank suppressed the increase in interest rates and economic activities to combat inflation; on the other hand, global headlines; predict that inflation, which was 8.7 percent in 2022, will decline to 6.8 percent in 2023 and to 5.2 percent in 2024. In other words, while the core (core) inflation is expected to decrease more gradually, an upward revision is expected to the 2024 inflation forecasts.
Decisive steps taken by authorities earlier this year to contain the turmoil in US and Swiss banking have drastically reduced the immediate risks of financial sector turmoil. Thus, the adverse risks to the outlook have also decreased. However, the balance of risks to global growth continues to progress downward. Suppose the Ukraine war, which has been on the agenda lately, intensifies, and there is a shock effect that triggers more restrictive monetary policies. In that case, inflation may remain high or even increase. While the reflection of this situation in the markets adapts to the economic policies implemented by the central banks, it may restart the turmoil in the financial sector.
Apart from all these, while there is a possibility that the debt problems of the states will spread to a broader economic group, inflation may decrease faster than expected in the increasing direction. This reduces the need for a tight monetary policy and may make domestic demand more flexible. When we look at most economic structures, the priority is to ensure financial stability on the one hand and to reduce continuous inflation on the other. Therefore, central banks should focus on restoring price stability and strengthening financial supervision and risk monitoring. In addition, countries should reduce the possibility of moral hazard in the event of market tensions and urgently accelerate the liquid flow. In this way, the improvements in the economy's supply side will ensure that inflation decreases towards the target levels in the fiscal consolidation.
Please click to wiev.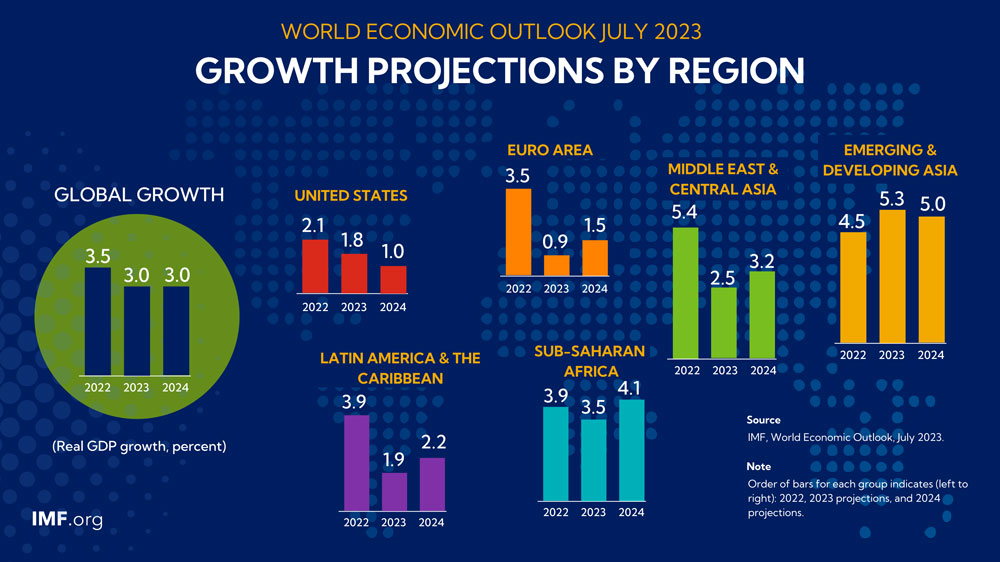

 Back
Back







