
Nilüfer MUTLU
Expert Chemist, UGM Test and Analysis Laboratory
Timing is very important for harvest. When the olive fruit starts to turn from green to purple, that is, when it starts to synthesize oil while benefiting from the sun to the maximum, the important health components such as polyphenols, triolein, olecanthal, and tocopherols in its structure are at the highest level. Therefore, early harvest should be done during this period to benefit from the bioavailability (polyphenols) in olive oil. Oil yield is low in early harvest; 1 liter of oil is obtained from 9-10 kg of olives. However, early harvest is an extremely beneficial period in terms of quality and health components.

Almost all of the world's olive production takes place in countries bordering the Mediterranean, such as Spain, Italy, Greece, Turkey, Tunisia, Syria, and Morocco. Our country is among the leading countries in terms of both the number of olive trees and olive production. Turkey's olive grove areas and number of trees are growing rapidly with various supports.
Olive oil is an oil obtained from olive tree (Olea Europea) fruits, without damaging their structure, as a result of mechanical and physical processes such as "Washing, Crushing, Kneading, centrifuging and filtering" in a suitable heat environment.
Have you heard that olives are the only fruit that is processed and oil is extracted only by mechanical means?
No heat treatment is used in the production of olive oil, nor is any solvent or chemical method used. One of the most important features that distinguishes olive oil from other vegetable oils is the method of extraction. Therefore, olive oil produced with the right technique is very important and valuable.
However, in oils obtained from plants such as sunflower, corn, peanut, hazelnut, rapeseed, and cotton, and even in all seed oils, chemical extraction methods with the help of solvents, namely a type of process that is not available in olive oil, are used to extract the oils.
In the Turkish Food Codex, olive oil is defined as "Oils obtained only from the fruits of the olive tree, Olea europaea L. Oils extracted using solvents or whose natural triglyceride structure has been changed by reesterification and mixtures with other oils are excluded from this definition."
CHEMISTRY OF OLIVE OIL…
Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats (Triolein) and contains nutrients such as polyphenols (antioxidants), vitamin E (tocopherols), and squalene, which are beneficial for health. The fatty acids found in the formation of triglycerides in olive oil vary depending on the climatic and agricultural conditions of the region where the olive tree is located.
The main fatty acid components of olive oil, according to national and international specifications, are as follows:
Saturated Fatty Acids:
-Palmitic acid: 7.5-20.0%
-Stearic acid: 0.5-5.0%
Monounsaturated Fatty Acids:
-Oleic acid: 55.0-83.0%
-Palmitoleic acid: 0.3-3.5%
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids:
-Linoleic acid: 3.5-21.0%
-Linolenic acid: 0.0-1.0%
So, what are these components used for?
Oleic Acid: Monounsaturated fatty acids (Oleic acid) are found in significant amounts in olive oil. Although the presence of unsaturated bonds in the fatty acids gives oils a special biological quality, it also makes them vulnerable to oxygen and causes autoxidation. The speed of auto-oxidation is proportional to the number of double bonds present and is prevented depending on the structure and amount of antioxidant substances.
Squalene (Hydrocarbon): This compound, which has metabolic importance, is found in high amounts in olive oil. Squalene moisturizes the skin thanks to its antioxidant properties. It reduces redness and irritation on the skin by providing anti-inflammatory effects and also strengthens the immune system.
Aroma Components: The basic sensory properties of olive oil are aroma and taste. This sensory property is given by a group of aroma components and the formation of these components in the olive fruit occurs through a series of enzymatic reactions.


Polyphenols: Polyphenols are compounds that are formed as a result of a natural biochemical interaction that occurs during the mechanical breaking and kneading of the olive fruit and that makes olive oil what it is.
What are bioactive polyphenols (phenols that can be absorbed by the human body)? And at what stage do they come into play?
Polyphenols protect the olive tree and fruit against external factors, and they also have a very valuable and important place in terms of human health.
Because the antioxidant properties of polyphenols can reduce cellular damage by neutralizing free radicals in the body. In this way, it can have positive effects on anti-aging (delaying aging), anti-inflammatory (reducing inflammation), and cardiovascular health, and it has also been confirmed by scientific research that it is protective against cancer.
The most important point is that the polyphenol content of olive oil can determine the quality and type of the oil. Olive oils produced by the cold pressing method and less processed generally have higher polyphenol content. Polyphenols are a very key point in olive cultivation.
Polyphenols present in plants are synthesized in the plant to protect itself against attacks from external factors. If the olive tree is intervened from outside, that is, as a result of all kinds of nutrients, minerals, medicines, preservatives soil enrichment, etc. given to the olive tree and even sunlight being directed or adjusted directly to the olive trees, the olive fruit says; "Since someone thinks of me independently, I do not need to develop my defense system and protect myself." At this point, polyphenol synthesis stops and the olive tree does not synthesize the compounds that protect its defense system, thus disrupting the biodiversity balance.
Since we aim to benefit from the polyphonies mentioned above in olive oil, "slow agriculture", that is, agriculture that preserves the natural balance, gains importance.
One of the most important polyphonies is the oleocanthal molecule, which takes its name from the olive fruit. Its meaning is bitter aldehyde oil consisting of olea (oil), canth (bitter), and al (aldehyde).
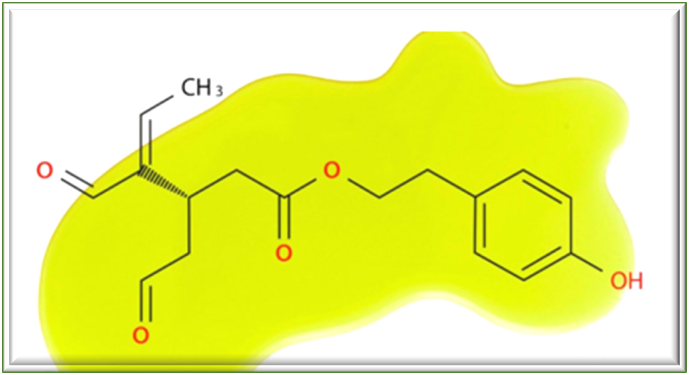
OLEACANTHAL…
Oleocanthal has been proven to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antimicrobial, anticancer, and neuroprotective activities. Oleocanthal is responsible for the bitter taste and sharpness that olive oil leaves in the oropharyngeal region of the throat. The dialdehyde functional groups in the molecule are responsible for the bitter taste.
The benefits of consuming good quality olive oil begin here. Because the bitter taste and sharpness are considered quality indicators. It has been suggested that the more intense the bitter taste, the stronger the anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects of virgin olive oil will be.
Antimicrobial compounds play an important role in the prevention of some infectious diseases. Oleocanthal, with its composition having strong anti-inflammatory activities, is a promising agent in the elimination of inflammatory and oxidative components that play a role in the pathogenesis of many chronic diseases. Although oleocanthal constitutes only 10% of olive and olive oil polyphenols, it is promising in preventing many metabolic disorders due to oxidative stress due to its effective biological activities.
While oleocanthal is mainly associated with beneficial effects on cancer and neurodegenerative diseases in research, new research suggests that this polyphenol also improves the health of people suffering from chronic cardiometabolic diseases, including obesity and diabetes.
In a study published in Spain in 2023, it was determined that consuming Natural (Extra Virgin Olive Oil) olive oil increases the antioxidant defense of the blood with the oleocanthal molecule and reduces oxidative stress and inflammation parameters.
OLIVE OIL TYPES…
The olive oil types according to the Turkish Food Codex (TGK) and the International Olive Oil Council (IOOC) are as follows:
a) Natural olive oil: Obtained from the olive tree fruit in a thermal environment that will not cause any change in its natural qualities, by applying only mechanical or physical processes such as washing, decantation, centrifugation, and filtration.
1) Natural extra virgin olive oil: Oils suitable for direct consumption, with a free fatty acidity of not more than 0.8 grams in terms of oleic acid per 100 grams, (FFA:%0.8)
2) Natural first olive oil: Oils suitable for direct consumption, with a free fatty acidity of not more than 2.0 grams in terms of oleic acid per 100 grams, (FFA:≤%2)
3) Crude olive oil/Refining: Oils with a free fatty acidity of more than 2.0 grams in terms of oleic acid per 100 grams and/or not suitable for direct consumption due to sensory and characteristic properties, suitable for refining or technical use, (FFA:≥2)
b) Refined olive oil: Oil obtained by refining raw olive oil with methods that do not cause changes in its natural triglyceride structure and with a free fatty acidity of not more than 0.3 grams in terms of oleic acid per 100 grams.
c) Riviera olive oil: It is an oil that is a mixture of refined olive oil and natural olive oils suitable for direct consumption and has a free fatty acidity of not more than 1.0 grams per 100 grams in terms of oleic acid.
ç) Flavored olive oil: It is an oil obtained by adding different spices, herbs, fruits, and vegetables to olive oils and has the characteristics of the products in its category within the scope of this Communiqué in terms of other characteristics.
HARVEST…
Harvest is the most exciting period in olive cultivation and a very important period in terms of olive oil quality and should be done consciously. Although modern harvesting machines and techniques have been developed according to the topographic structure and size of the lands, what we need the most is the human hand. The human hand is what gives the olive oil its spiritual taste.

Nowadays, battery-powered machines with combs that work with human and semi-human movement have also been developed.


The olive tree should never be hit with a stick because when the olives are harvested, the baby shoots of the next year are located on the tree branches. Therefore, the olives or harvest of the next year are shaped in a way while harvesting.
WHAT IS EARLY HARVEST OLIVE OIL?
The timing is very important for harvest. When the olive fruit starts to turn from green to purple, that is, when it starts to synthesize oil while benefiting from the sun to the maximum, the important health components such as polyphenols, triolein, oleocanthal, tocopherols in its structure are at the highest level. Therefore, early harvest should be done during this period to benefit from the bioavailability (polyphenols) in olive oil. Oil yield is low in early harvest; 1 liter of oil is obtained from 9-10 kg of olives. However, early harvest is an extremely beneficial period in terms of quality and health components.

The characteristics of olive oil produced by early harvest are as follows:
- It has a low acidity. (Acidity increases as the olive ripens.)
- It differs from other olive oils with its more intense fruit flavor/aroma and smell.
- It contains high amounts of chlorophyll and phenolic compounds (components with antioxidant properties), which are elements that strengthen the immune system and extend the shelf life of the oil.
- They are rich in vitamin E, so they have cell regenerative properties and thus protect the body against aging.
- It reduces the risks of obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension.
- It lowers bad cholesterol levels and increases good cholesterol levels.
- It regulates glucose metabolism in diabetic patients.
OLIVE OIL STORAGE CONDITIONS…
The basic factors to consider when storing olive oil are light, oxygen, temperature, air, and time. The most ideal way to store olive oil is in ceramic or dark glass bottles that are not humid, at room temperature, and tightly closed.
It should not be stored in the refrigerator because although it contains monounsaturated fats, olives also have some saturated fat in their structure. The oil that freezes in the refrigerator melts again when brought to room temperature. The structure of olive oil that is constantly melted and frozen deteriorates over time.
TERMINOLOGY IN OLIVE OIL: THE ART OF READING LABELS…
Which is the right olive oil?
1-First Quality Olive Oil: Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)
It is divided into two early harvest and late harvest. So when we choose a quality olive oil, it should be natural extra virgin olive oil. The second question that should come to our mind is: Early harvest or late harvest? As we mentioned above, our preference should be for early harvest, its taste is very fruity and its acidity is a maximum of 0.8%.
2-Second quality olive oil: Natural first olive oil (Virgin Olive Oil VO)
Although it is mentioned first in its name, according to the Turkish Food Codex, it is of lower quality than natural extra virgin olive oil. Since this type of oil is produced the most in our country, it is called natural first olive oil as a marketing technique. Here, free acidity is up to 2% and it does not have a fruity taste. It can be eaten and packaged directly.
3-Third quality Olive Oil: Lampant
Free fatty acids are more than 2%, it does not have a fruity taste and It is flawed, and even an oil that cannot be eaten directly. This is raw olive oil. This olive oil is brought to an edible form by adjusting its acidity in a refinery, changing its triglyceride structure, and adjusting its smell and color with chemical methods. If 1% natural extra virgin or natural first oil is added to this processed oil, the resulting oil is the Riviera we all know. It is an oil that has been completely changed in structure, adjusted in acidity and does not contain any natural fruity taste or health components. It is an ideal oil to use in frying because its smoke level and flame temperature (210 0C) are quite high.
To summarize all of what we have said; the most important criterion that determines that olive oil is of good quality is its fruitiness (natural bitterness). It should be natural extra virgin olive oil (Extra Virgin Olive Oil) produced with early harvest. Therefore, when buying olive oil, it is useful to pay attention to the polyphenol value along with the production technique and acidity value.
WHAT IS ADULTERY IN OLIVE OIL, HOW IS IT DETECTED?
In the analysis of olive oil and vegetable oils, different analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), and UV spectrophotometer titrimetric are used together (combined) in the determination of parameters such as fatty acid methyl ester composition (FAME), free fatty acid (FFA), sterol, aroma components, ECN42.
It is extremely easy to mix olive oil with other oils, i.e. adulteration. The most important adulteration sources for natural olive oil are seed oils (sunflower, poppy, soy, cotton, corn, etc.), vegetable refined mixed oils, hazelnut oil, and second extraction oils, which are derivatives of olive oil itself, and refined pomace oils.
It is very easy to detect this under laboratory conditions. Spectrophotometric methods determine whether a different type of oil has been mixed into olive oil under UV light.

I will end my article by quoting a passage from Nazim Hikmet's poem “'About Living”:
I mean, you have to take life so seriously,
Even at seventy, for example, you will plant olives,
And not just for the kids,
For not believing in death even though you're afraid of dying,
It's because the living part of it is predominate.

KAYNAK:
Callao, M. P., & Ruisánchez, I. (2018). An overview of multivariate qualitative methods for food fraud detection. Food Control, 86, 283–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.11. 034
Gurdeniz, G., & Ozen, B. (2009). Detection of adulteration of extra-virgin olive oil by chemometric analysis of mid-infrared spectral data. Food Chemistry, 116(2), 519– 525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.0 2.068
Pan, M., Sun, S., Zhou, Q., & Chen, J. (2018). A Simple and Portable Screening Method for Adulterated Olive Oils Using the Hand-Held FTIR Spectrometer and Chemometrics Tools. Food Chemistry, 0, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750- 3841.14190
2-Neoskola: Zeytinyağı üretim teknikleri eğitimi
3-Resmi Gazete: Türk Gıda Kodeksi Zeytinyağı Tebliği
 Back
Back